Casting Industry Trends
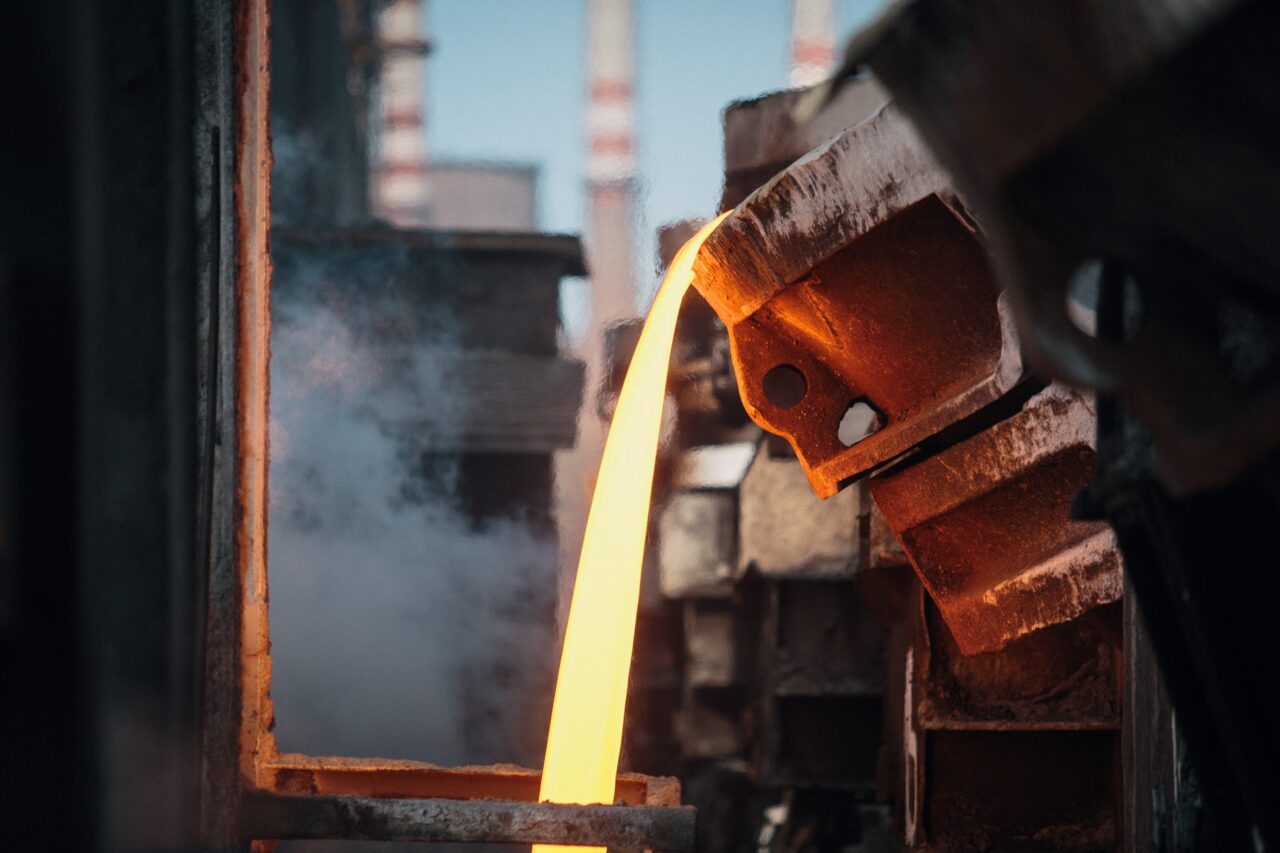
In simple terms, a foundry is a factory where castings are made by melting metal, pouring the liquid metal into molds, and letting it solidify. Even if you have never visited a foundry or seen one, you are likely surrounded by the metal castings they produce. There’s a good chance that you are currently reading this within a short distance of one.
Foundries do more than just produce metal parts for engines, railroads, or pipes. They also create components for machines that are necessary in the manufacturing of many essential consumer products on which we rely. In fact, 90 percent of all manufactured goods depend on metal castings.
Castings are being produced in foundries all around the world. Each country and even each foundry might have varying conditions, but the industry as a whole is experiencing certain trends. These shifts in the foundry industry have significant impacts on quality and cost for the end user. Over the years, there have been advancements in foundry technologies, and basic foundry operations have also transformed and diversified. Among the most dominant trends are scale, automation, and on-site finishing.
The introduction of new, larger, safer, and more efficient furnaces has allowed the industry’s output to grow, despite the gradual decrease in the number of North American foundries. Even though the United States has fewer foundries than India and Japan (see table), it ranks second globally in terms of cast metal production, with an output of 12,250,000 metric tonnes. China takes the lead, far surpassing all competition, with an impressive annual production of over 44,500,000 metric tonnes.
Blog - ETC Foundry | The Engineer's Blueprint: Building a Better Tomorrow
Bring to the table win-win survival strategies to ensure proactive domination. At the end of the day, going forward, a new normal that has evolved from generation.
UAE
Headquarters
ETC Foundry
Emirates Technology Castings FZE
PO BOX 49911
Hamriyah Free zone, Sharjah.
United Arab Emirates
LOCATIONS
We Are Here